Patient Education
We offer general dentistry services for all age groups.
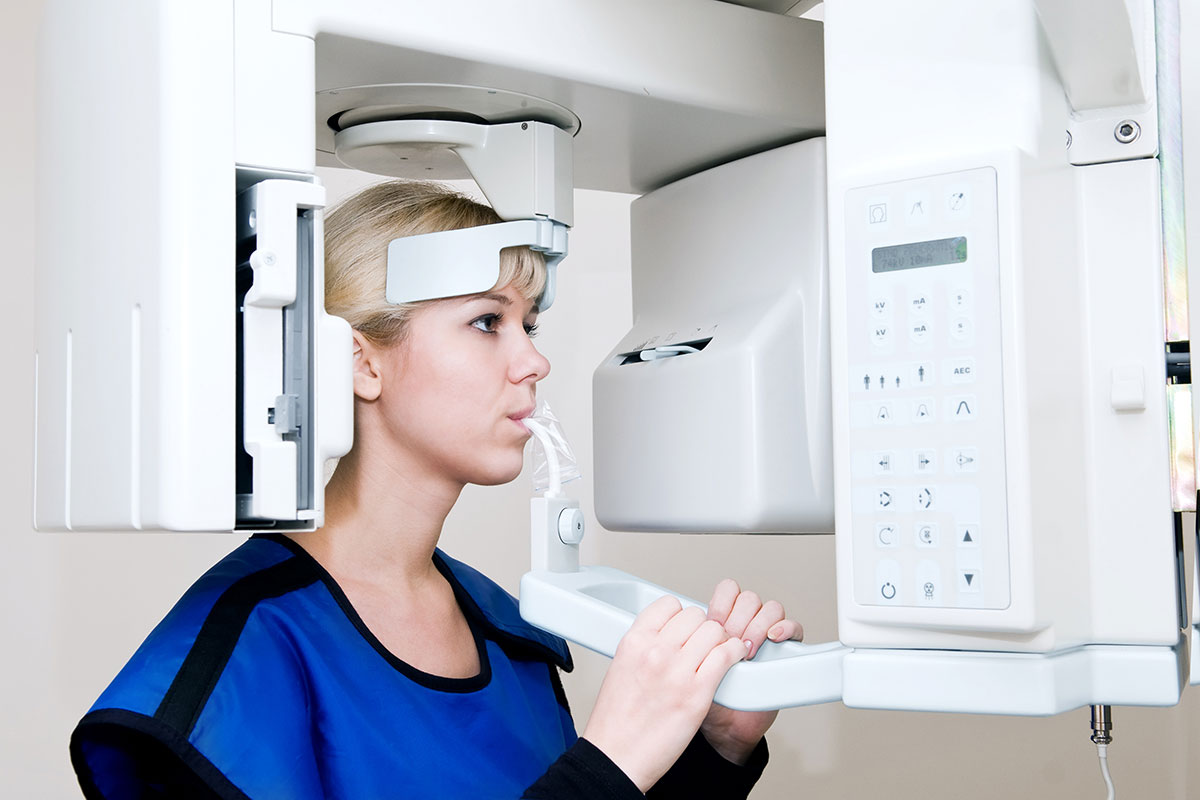
Full Mouth Exam and X-Rays
We will take a panoramic X-ray and perform a comprehensive exam of your full mouth. We will discuss your dental health and provide you with an estimated treatment plan and fee if needed.
Panoramic X-ray: This image gives us a good view of all the soft and hard tissue of your oral cavity. It takes less than one minute to complete and greatly reduces the amount of radiation to which our patients are exposed.
Bitewing X-rays: To compliment the panoramic X-ray we get a set of bitewing, or “cavity detection”, X-rays that allow the doctors to see in between your back teeth. This is one of the most common spots for cavities to develop. Bitewing X-rays are composed of two X-rays on each side of the mouth.
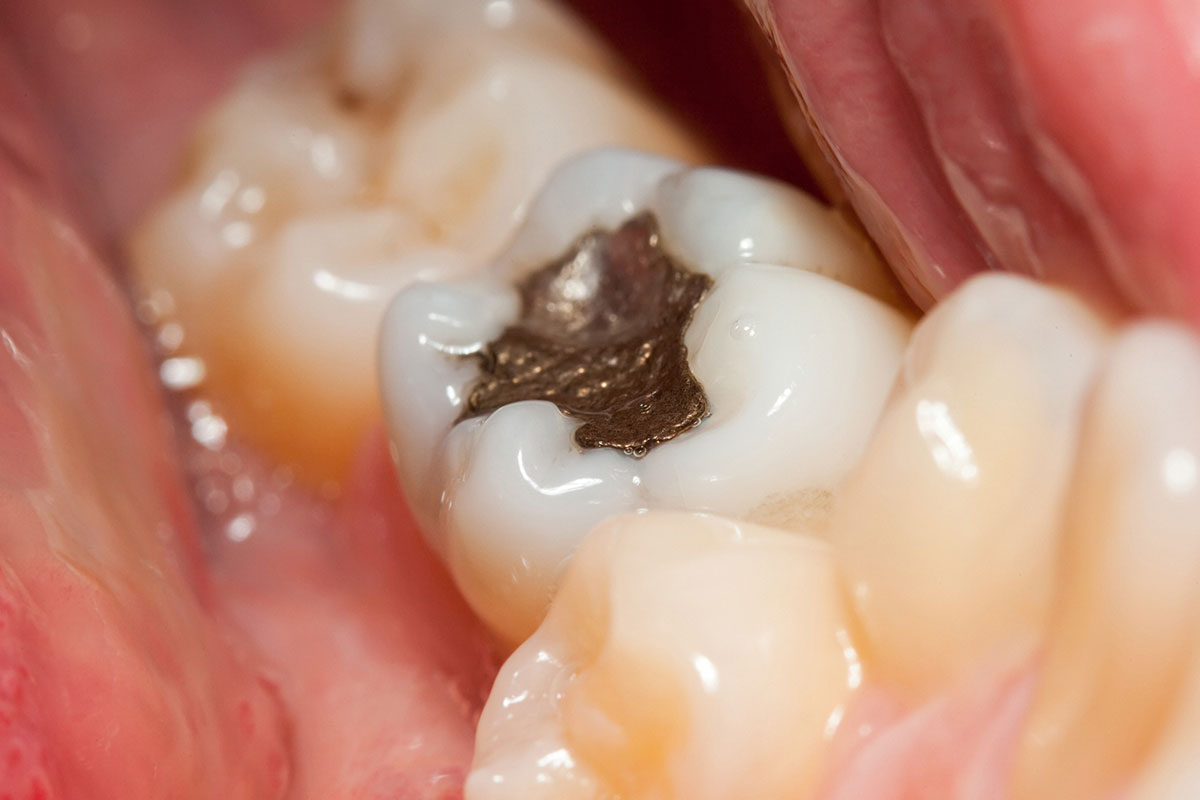
Filling/Restoration
When you come for a dental exam, our dentist checks your fillings and may suggest that you replace any loose or broken ones. Your dentist also looks for signs of decay, such as brown or black spots and may want to use X-rays to take a closer look at problem spots.
If you have a cavity, your dentist may keep an eye on it (if it’s small) or fill it right away. If a large cavity is not filled, it can get bigger and cause pain. The tooth may even have to be removed and replaced with a false (or artificial) tooth. If you have a cavity and it needs a filling, there are different kinds of fillings to do the job.
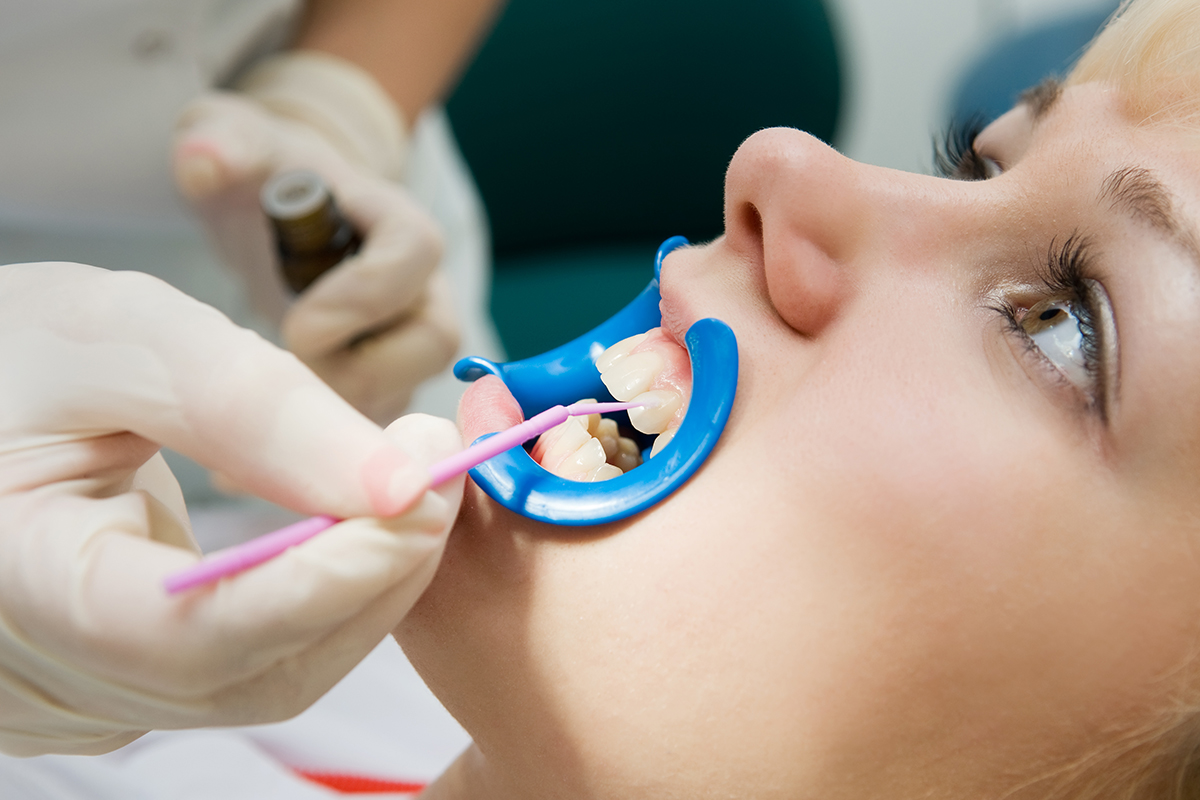
Sealants
Dental Sealants are a plastic coating placed on the biting surface of the teeth. They are very effective in preventing tooth decay. Sealants work by filling in the crevasses on the chewing surfaces of the teeth. This shuts out food particles that could get caught in the teeth, causing cavities.
The application is fast and comfortable and can effectively protect teeth for many years.
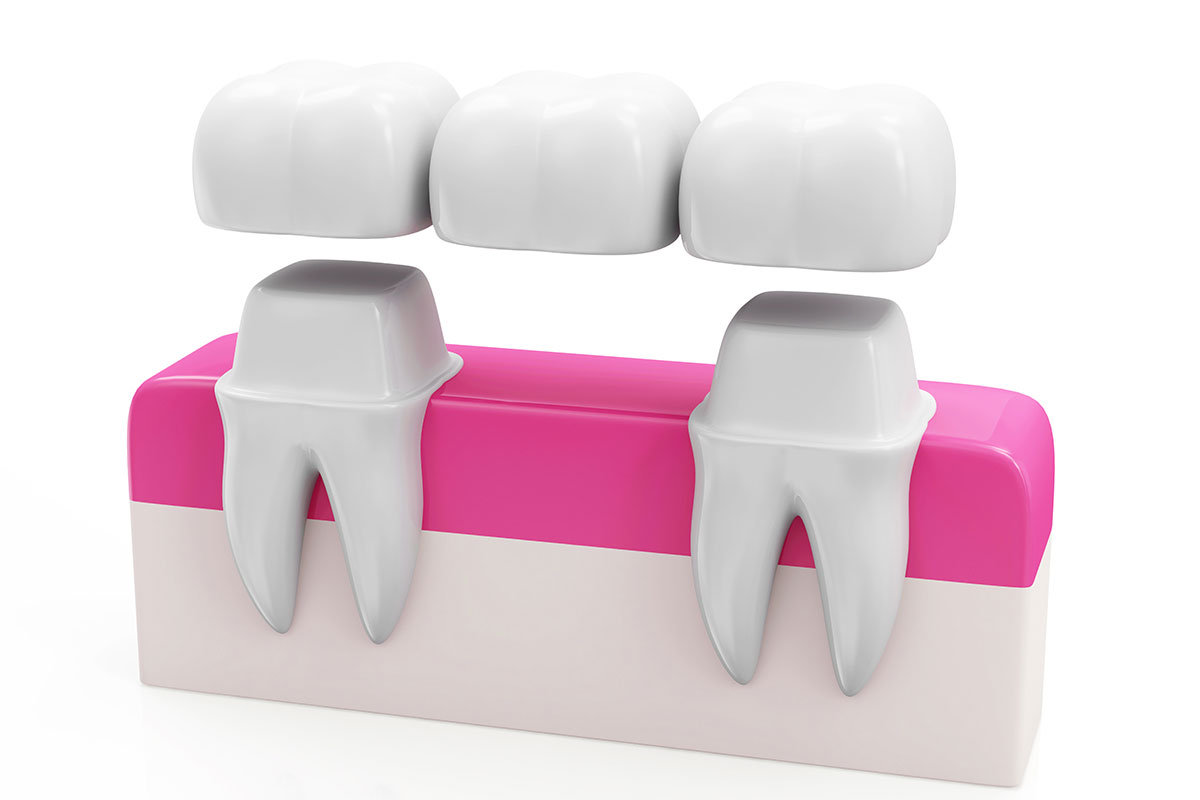
Bridges
Bridge is a false tooth that is fused between two porcelain crowns to fill in the area left by a missing tooth. The two crowns holding it in place are attached onto your teeth on each side of the false tooth and the bridge is not removable because it is secured into place.
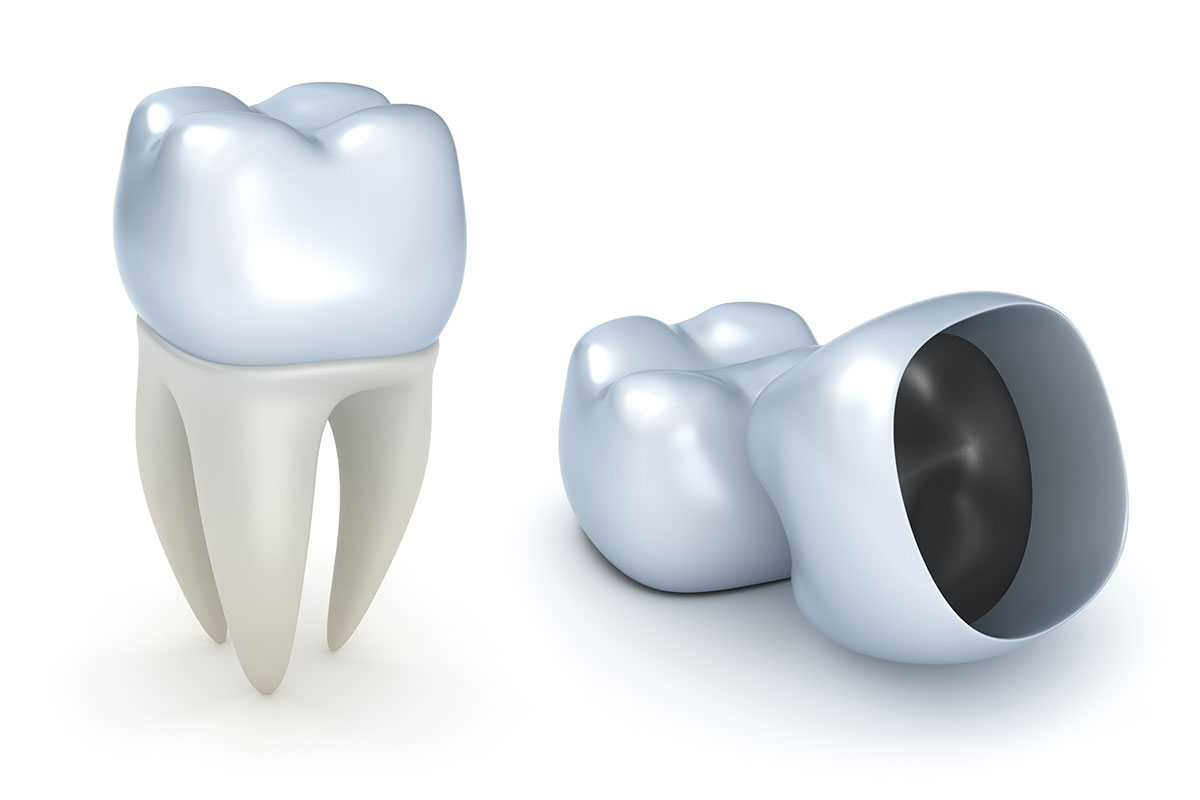
Crowns
If your tooth is damaged but not lost, a crown can be used to restore its shape, appearance and function. You may need a crown if you have a root canal, a large filling in a tooth or a broken tooth. A crown, also called a cap, is a hollow, artificial tooth used to cover a damaged or decayed tooth.
The crown restores the tooth and protects it from further damage. Crowns can also be used to cover a discoloured or misshapen tooth. A tooth that has been fixed with a crown looks and works very much like a natural tooth.
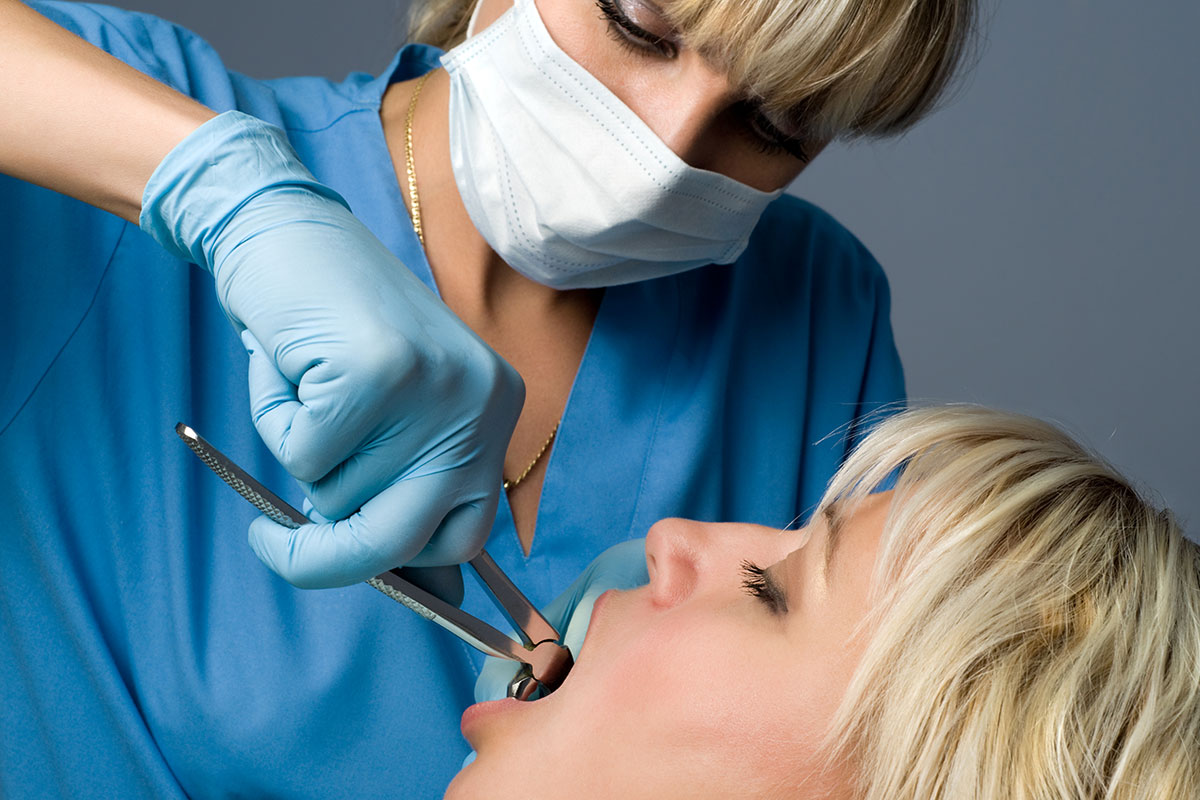
Tooth Extractions
A tooth that is severely damaged may need to be removed. Before removing your tooth, our dentist will give you a local anesthetic to numb the area where the tooth will be removed. A stronger, general anesthetic may be used, especially if several or all of your teeth need to be removed.
General anesthetic prevents pain in the whole body and will make you sleep through the procedure.
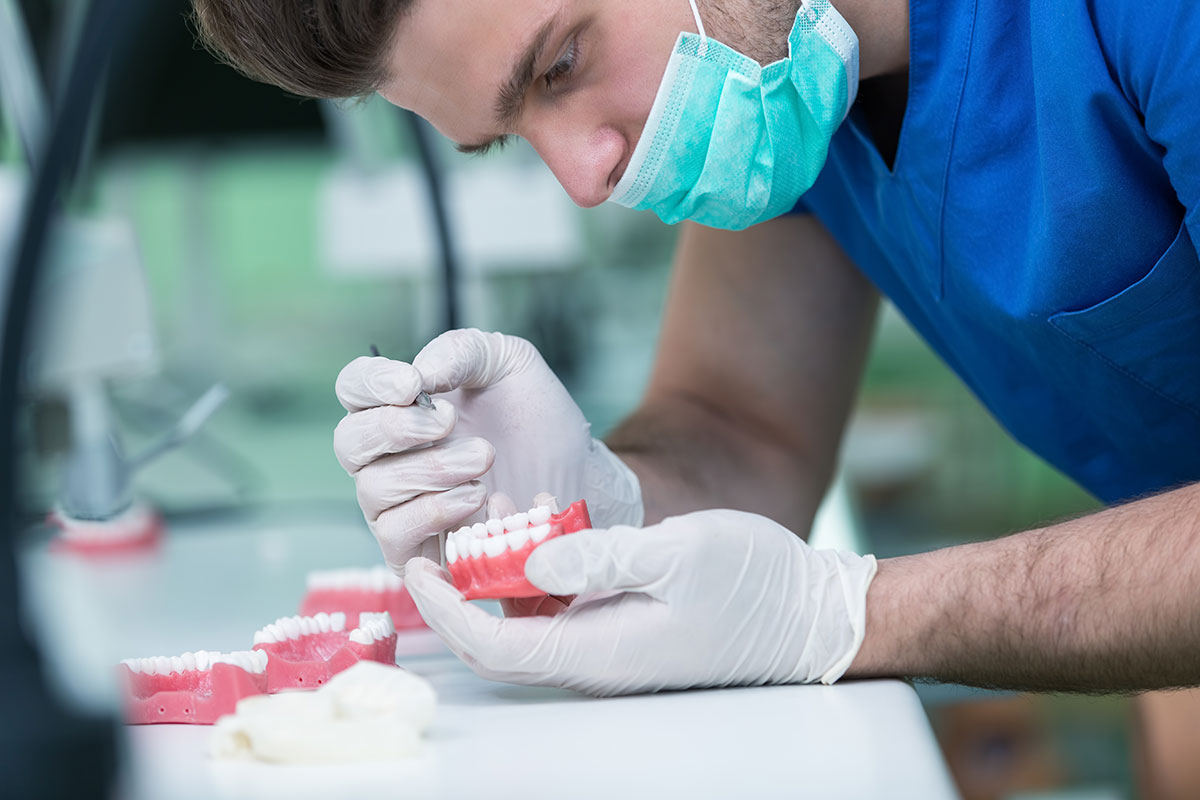

Dentures
A denture is a removable replacement for missing teeth and the tissues connected to those teeth. It is made of acrylic plastic and sometimes porcelain and metal materials. A denture closely resembles natural gum tissue and teeth.
A partial denture is for people who still have some of their natural teeth. Complete dentures replace all of the teeth, while partial dentures fill in the spaces created by missing teeth and prevent other teeth from shifting position.
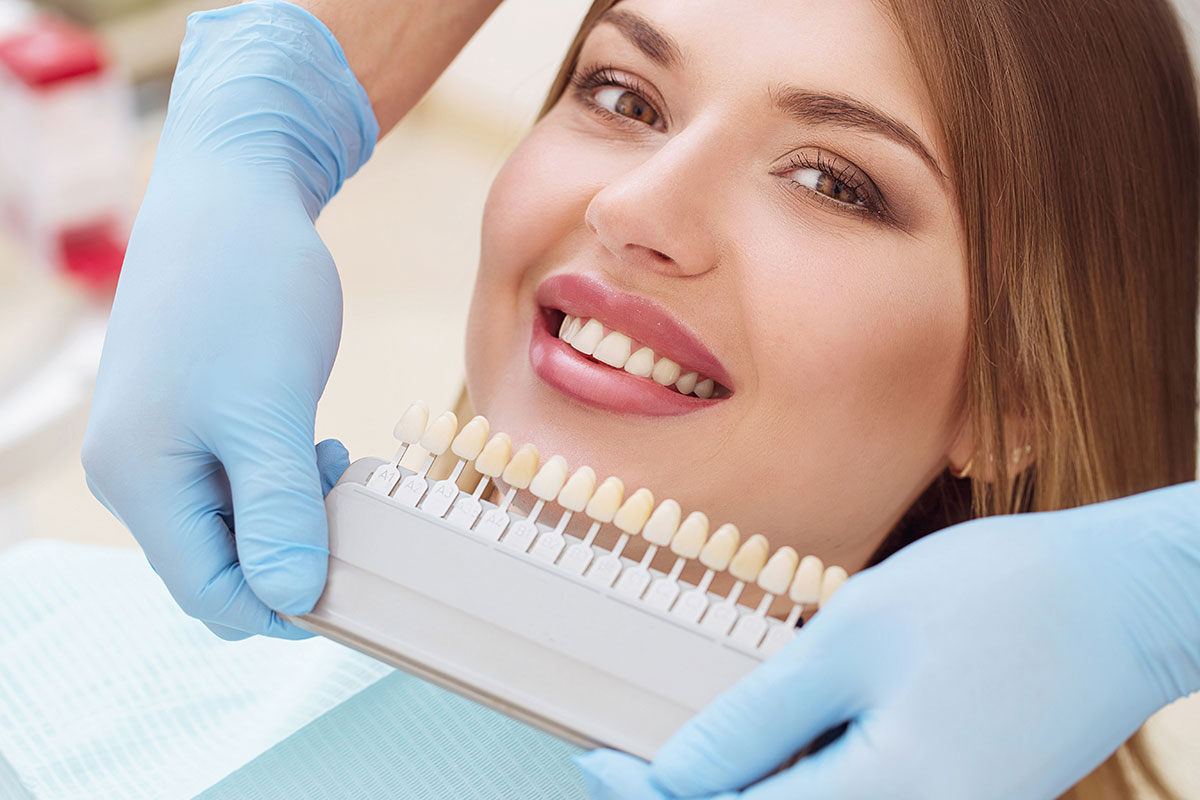
Teeth Whitening
There are many options to consider if you want to obtain whiter teeth and a more attractive smile. In-Office Bleaching- For those who are candidates for bleaching, our dentist may suggest chairside bleaching, which may require more than one office visit.
Each visit may take from 30 minutes to one hour. During chairside bleaching, the dentist will protect the oral soft tissues with either a protective gel or a rubber shield. A bleaching agent is then applied to the teeth, and a special light may be used to enhance the action of the agent.
Bleaching solutions contain peroxide(s), which bleach the tooth structure. They typically come in a gel and are placed in a mouthguard. The dentist can make a custom-fitted mouthguard that will fit the teeth precisely, ensuring a more uniform and effective action.
In-Home Bleaching- There are several types of products available for use at home, which can either be dispensed by your dentist or purchased over-the-counter. While these products have improved over the years in effectiveness and ease of use, professional supervision increases success with home bleaching, ensuring proper fit of trays, diagnosis of discoloration and chance of success with bleaching, monitoring progress and managing side effects (sensitivity).

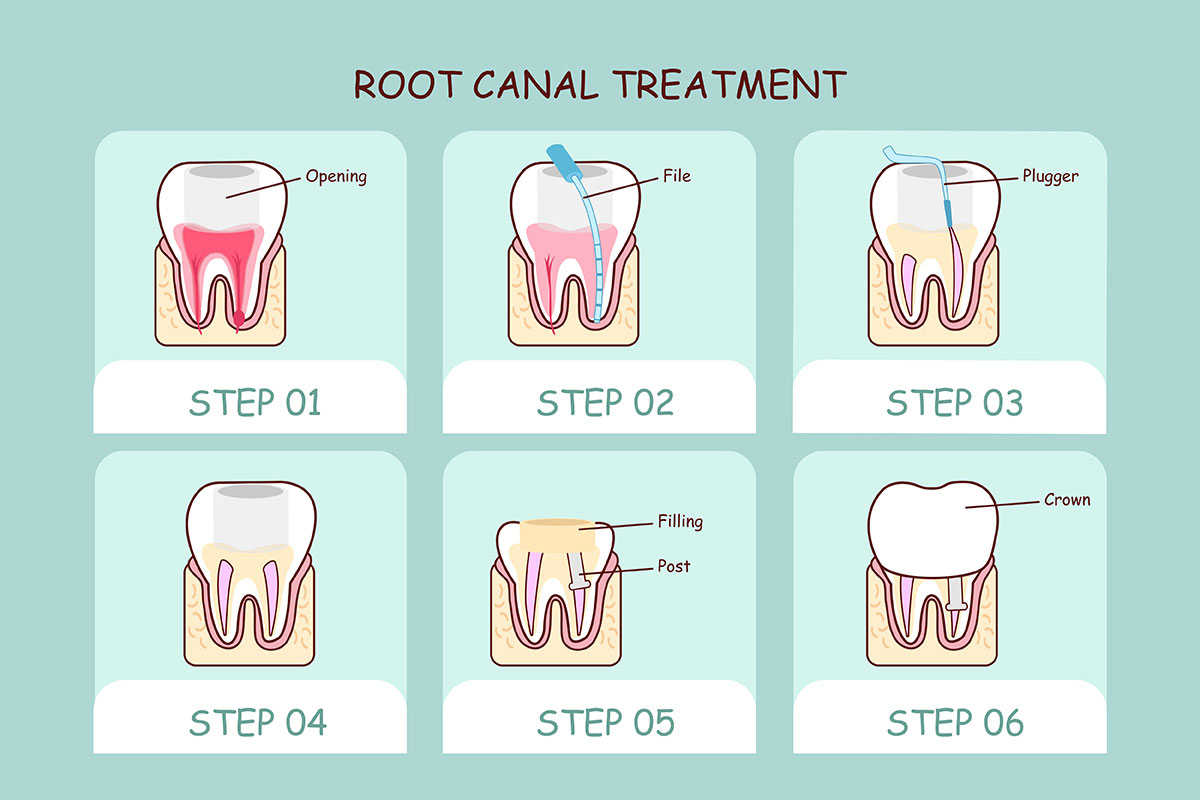
Root Canal
A root canal is a dental procedure to remove dead or dying nerve tissue and bacteria from inside a tooth. A root canal is done if you have an infection that affects the nerve in the root of a tooth. Generally, there is pain and swelling in the area.
The infection can be the result of a tooth crack, cavity, or injury. A root canal can save your tooth. Without treatment, the tooth may become so damaged that it must be removed.
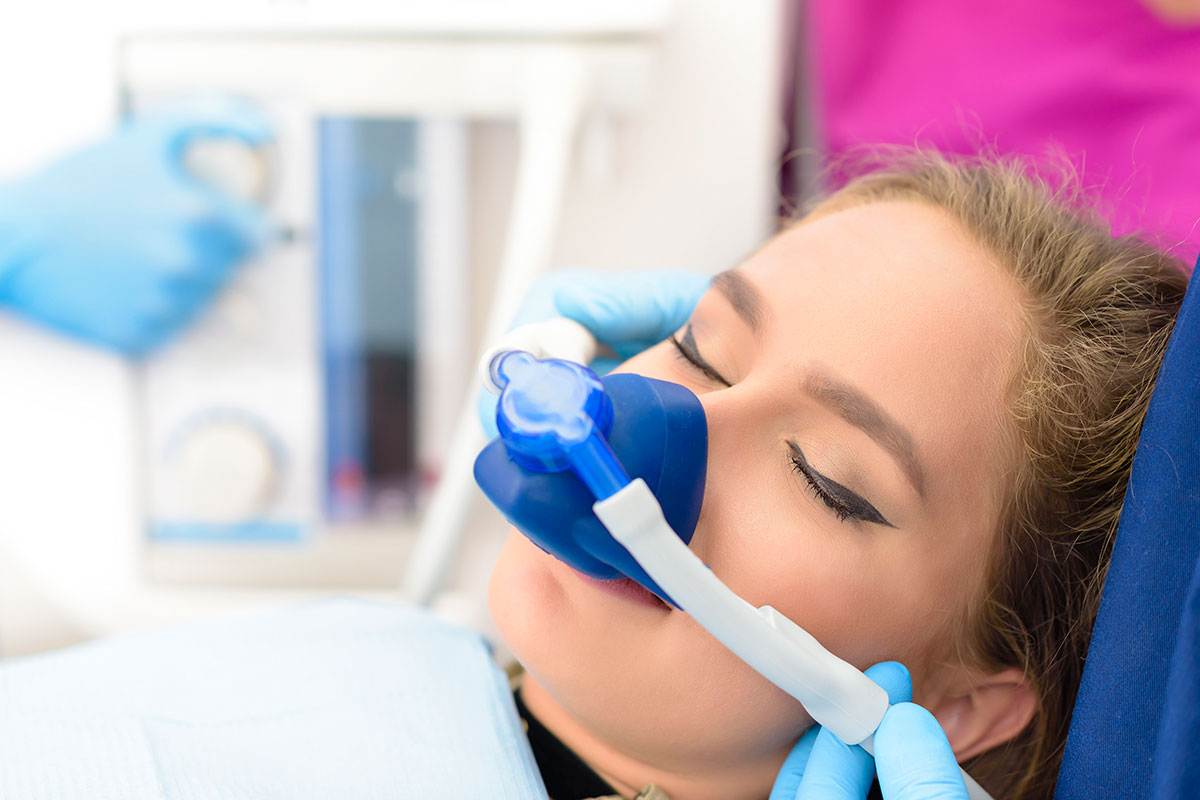
Sedation
Sedation allows dentists to create a state of relaxation and thus manage the fear and pain patients may experience during dental procedures. There are several different types of sedation in dentistry. Local anesthesia is administered by injecting medication into tissue or by applying a medication topically to an area to eliminate sensation.
Minimal sedation is used most frequently in dentistry and usually involves taking medications orally. All bodily functions remain normal and the person is able to breathe on his or her own.
The patient may respond normally to verbal commands and may experience some degree of amnesia about what happened during their dental appointment. Nitrous oxide or “laughing gas” may be used to achieve minimal sedation and in combination with a recommended dosage of oral medication.
Moderate sedation is achieved by using medications that can be taken orally or intravenously (IV). Patients who undergo moderate sedation are awake and respond to touch and/or verbal commands. All bodily functions remain normal, and the patient does not need assistance breathing.
Deep sedation can be achieved by injecting medication, giving oral medications, and in combination with gases. Patients who are deeply sedated are not easily awakened but may respond to some stimulation. Patients may need some breathing assistance at deeper levels.



